662. 二叉树最大宽度
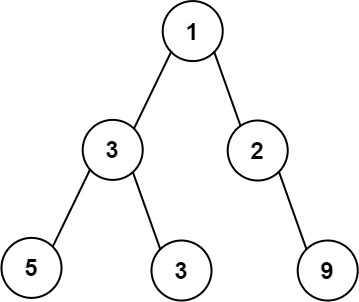
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/ 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。 树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。 每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,这些 null 节点也计入长度。 题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。 示例 1:
输出:4
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9) 。示例 2:
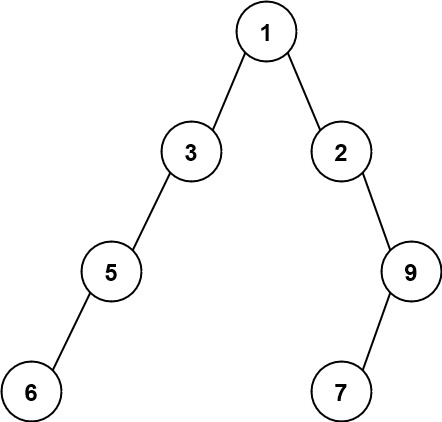
输出:7
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 7 (6,null,null,null,null,null,7) 。示例 3:
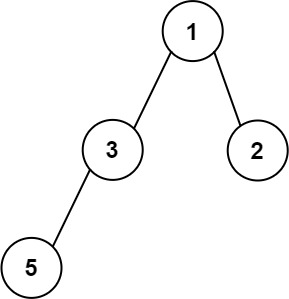
输出:2
解释:最大宽度出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2) 。提示:
- \(树中节点的数目范围是 [1, 3000]\)
- \(-100<=Node.val<=100\)
# 题解
解法一:广度优先遍历(官方题解)
|
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:\(O (n)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O (n)\)
解法二:深度优先遍历(官方题解)
using ULL = unsigned long long; |
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:\(O (n)\)
- 空间复杂度:\(O (n)\)

Invitation
x-17
202111170521
created:2021/11/17
Welcome to X
月缺不改光,剑折不改钢
共矜然诺心,各负纵横志
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 潇十七!
评论